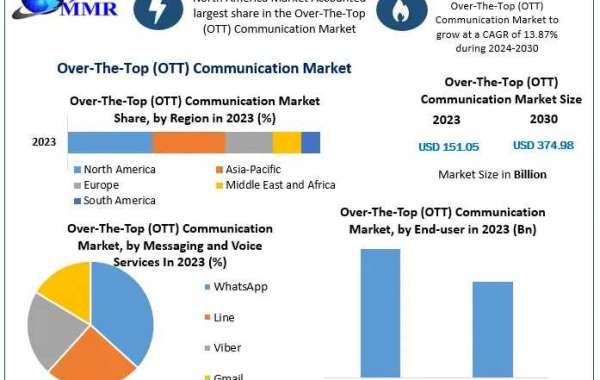
Over-The-Top Communication Market Overview
Over-the-top communication services have revolutionized the way people interact across the globe. These services allow users to communicate via messaging, voice, and video over the internet, bypassing traditional telecommunication networks. With the rapid proliferation of smartphones, broadband connectivity, and changing user preferences, the OTT communication market is witnessing explosive growth.
What is OTT Communication?
OTT communication market Trends refers to the delivery of communication services directly to users via the internet, without the need for traditional telecom infrastructure. Examples include WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, Skype, Zoom, Telegram, and Signal. These platforms offer instant messaging, voice and video calls, and group chats—often at no cost—making them a preferred choice for both personal and business communication.
Market Size and Growth Drivers
Smartphone Penetration: The increasing number of smartphone users worldwide, particularly in emerging economies like India and Southeast Asia, has expanded the user base for OTT platforms.
High-speed Internet Access: Widespread adoption of 4G and 5G networks has significantly improved the quality and reliability of OTT services.
Changing User Preferences: Consumers increasingly favor flexible, real-time communication without being tied to telecom plans or costly international calling rates.
Remote Work and Virtual Collaboration: The COVID-19 pandemic permanently altered work habits, boosting the use of OTT video conferencing platforms such as Zoom and Microsoft Teams.
Innovations and Features: The continuous addition of features like end-to-end encryption, stickers, file sharing, AI-powered chatbots, and multi-device support enhances user engagement.
Challenges in the Market
Despite its rapid expansion, the OTT communication market faces several challenges:
Data Privacy and Regulation: Governments around the world are increasingly scrutinizing how these platforms handle user data. Regulatory compliance, especially with laws like GDPR and India's IT rules, remains a complex task.
Monetization: While many OTT services are free, monetizing large user bases without alienating them is a delicate balance. Ads, subscription models, and in-app purchases are common strategies.
Competition with Telecom Operators: Traditional telecom providers see OTT services as a threat to their revenue streams from voice and SMS, leading to regulatory lobbying and efforts to integrate OTT-like services within their networks.
Conclusion:
The OTT communication market Size stands as a powerful testament to the digital age disruptive, scalable, and indispensable. As consumer expectations evolve, only those platforms that adapt swiftly and responsibly will remain at the forefront of this communication revolution.